Software as a service (SaaS) is a cloud computing service model that delivers software applications over the internet. A third-party provider hosts the application and makes it available to end-users on a subscription basis. This eliminates the need for users to install and maintain software on their own devices, freeing them to focus on utilizing the application’s functionality.
SaaS is a rapidly growing market, transforming how businesses and individuals access and use software. This article delves into the intricacies of Saas Services, exploring their architecture, benefits, challenges, security considerations, and future trends.
Understanding SaaS Architecture
SaaS applications are typically accessed through a web browser, simplifying user access and eliminating complex installation procedures. Two primary architectures underpin SaaS services:
Multi-Tenant Architecture
In a multi-tenant architecture, a single instance of the SaaS application serves multiple customers (tenants). Each tenant’s data is isolated, ensuring security and privacy, while sharing the underlying infrastructure and platform. This model allows for efficient resource utilization, streamlined updates, and cost-effectiveness for both the provider and the customers. This architecture allows the provider to efficiently manage maintenance, updates, and bug fixes for all users simultaneously.
Single-Tenant Architecture
Alternatively, a single-tenant architecture provides each customer with a dedicated instance of the software application. This offers greater customization and control, but comes at a higher cost due to increased resource allocation and management overhead. This model is often preferred by organizations with stringent security or compliance requirements.
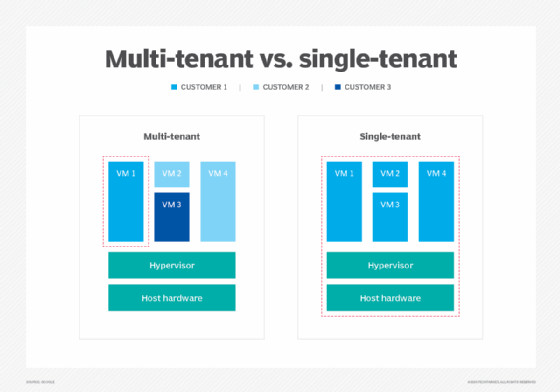 multi-tenancy and single-tenancy diagram
multi-tenancy and single-tenancy diagram
Advantages of SaaS Services
SaaS offers numerous benefits over traditional on-premise software:
- Cost Savings: Eliminates upfront hardware and software licensing costs, transitioning to a predictable subscription model.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Reduced IT Burden: Frees internal IT teams from software maintenance and updates, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Automatic Updates: Ensures users always have access to the latest features and security patches without manual intervention.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Enables access from any internet-connected device, fostering collaboration among users.
- Enhanced Security: SaaS providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and expertise, often surpassing the capabilities of individual organizations.
Challenges and Risks of SaaS Services
While SaaS offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges:
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating data and processes to a new vendor can be complex and costly.
- Security Concerns: Reliance on a third-party provider necessitates careful evaluation of their security practices and compliance certifications.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating SaaS applications with existing systems may require custom development or specialized integration tools.
- Downtime Risk: Service disruptions can impact business operations, highlighting the importance of service level agreements (SLAs).
- Data Governance and Compliance: Understanding data residency and compliance requirements is crucial, especially for industries with strict regulations.
SaaS Security and Privacy
Security is paramount in the SaaS landscape. Providers employ various measures to protect user data:
- Encryption: Protects data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Control: Restricts access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
- Security Monitoring: Detects and responds to potential threats in real-time.
- Compliance Certifications: Adherence to industry standards and regulations (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2) provides assurance of security practices.
Organizations should also implement their own security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and employee training, to enhance overall security posture.
The Future of SaaS Services
SaaS is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by trends like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into SaaS applications to automate tasks, personalize user experiences, and provide intelligent insights.
- Vertical SaaS: Specialized SaaS solutions tailored to specific industries are gaining traction.
- Focus on Customer Success: Providers are increasingly prioritizing customer onboarding, training, and support to ensure successful adoption and maximize value.
 cloud service model diagram
cloud service model diagram
Conclusion
SaaS services have revolutionized software delivery and consumption, offering a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional software models. While challenges exist, the benefits of SaaS are compelling, driving widespread adoption across various industries. By understanding the key aspects of SaaS, organizations can leverage its power to enhance productivity, innovation, and competitiveness. As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, embracing emerging trends will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of this transformative technology.