The history of the Olympic Games is a captivating journey from ancient Greece to the modern era, demonstrating its lasting legacy of sportsmanship. If you are in the USA and experiencing issues with your Polar device and require reliable support, visit polarservicecenter.net for comprehensive solutions. This guide explains how the games evolved from religious festivals to international sporting events, highlighting the journey and what to expect from the summer and winter games, including related equipment.
1. What are the origins of the Olympic Games?
The Olympic Games originated in ancient Greece nearly 3,000 years ago, with the earliest recorded games held in Olympia. These games were part of a religious festival honoring Zeus, held by the city-state of Elis in the northwestern Peloponnese. The games quickly grew into a tradition and historians began measuring time by the four-year interval between them, known as an Olympiad.
1.1 How did the ancient Greek sporting festivals evolve?
By the end of the 6th century BCE, at least four major Greek sporting festivals had risen to prominence:
- The Olympic Games at Olympia
- The Pythian Games at Delphi
- The Nemean Games at Nemea
- The Isthmian Games near Corinth
These festivals spread to nearly 150 cities, including Rome, Naples, and Alexandria.
1.2 What was the significance of the Olympic Games in ancient Greece?
Of all the Greek games, the Olympics were the most celebrated. Held every four years between August 6 and September 19, these games held such a central place in Greek history that historians used the Olympiad, the interval between each celebration, to measure time. They were an essential part of a religious festival, held in honor of Zeus at Olympia.
1.3 Who was the first Olympic champion, and when did he win?
The first Olympic champion recorded in the records was Coroebus of Elis, a cook. He won the sprint race in 776 BCE. Legends suggest the Games began earlier, with Heracles (son of Zeus and Alcmene) credited as a founder.
2. What competitions were featured in the ancient Olympic Games?
Initially, the ancient Olympic Games featured only one event: a footrace. Over time, additional events were added, including wrestling, the pentathlon, boxing, and chariot racing. The program was eventually diversified to include events for boys, heralds, and trumpeters.
2.1 What were the original athletic events in the ancient Olympics?
In 776 BCE, the only event was a footrace called the stade, covering one length of the track at Olympia (about 192 meters). Over the years, new races were added:
- Diaulos: A two-length race (similar to the 400-meter race)
- Dolichos: A long-distance race (comparable to modern 1,500- or 5,000-meter events)
2.2 When were wrestling and the pentathlon introduced?
Wrestling and the pentathlon were introduced in 708 BCE. The pentathlon comprised five events:
- Long jump
- Javelin throw
- Discus throw
- Footrace
- Wrestling
2.3 What was the pancratium, and when was it included in the Olympics?
The pancratium, a no-holds-barred combat sport combining wrestling, boxing, and street fighting, was introduced in 648 BCE. Kicking and hitting a downed opponent were allowed, but biting and gouging were forbidden.
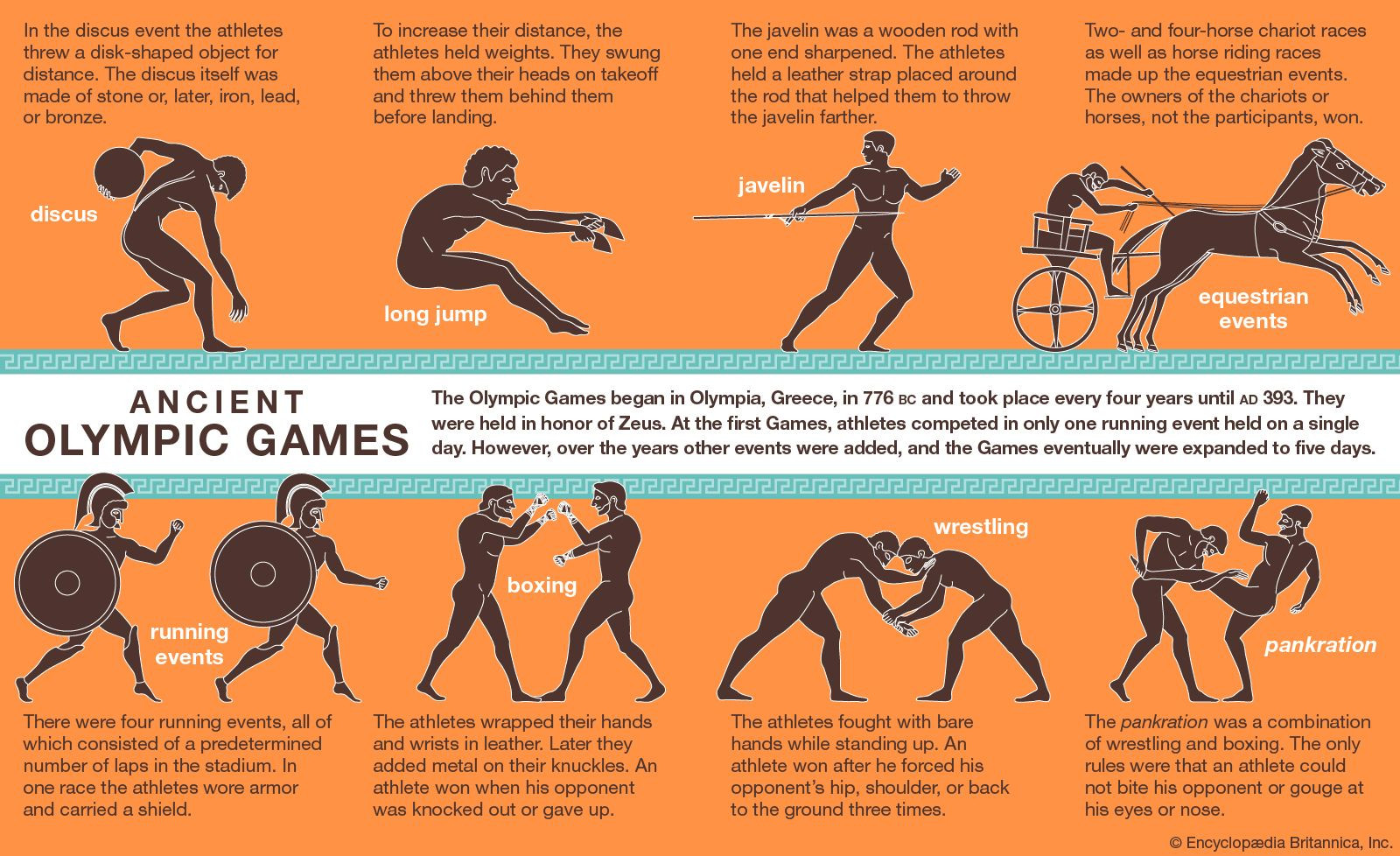 Athletes competing in the pankration during the ancient Olympic Games
Athletes competing in the pankration during the ancient Olympic Games
2.4 How long did the ancient Olympic Games last, and what was the closing ceremony like?
In the early centuries, all contests occurred on one day. Later, the Games extended to four days, with a fifth day for the closing ceremony, presentation of prizes, and a banquet for the champions.
2.5 What are the main differences between ancient and modern Olympic Games?
Team sports and ball games were absent in ancient Olympics, while the track and field events were limited to the four running events and the pentathlon. Events such as chariot races and horse racing took place in the hippodrome, south of the stadium.
3. What was the status of athletes in the ancient Olympic Games?
The Olympic Games were exclusive to freeborn Greeks, including those from colonies in the Italian peninsula, Asia Minor, and Africa. Most participants were professionals who trained full-time.
3.1 Who was eligible to compete in the ancient Olympic Games?
Technically, only freeborn Greeks could participate. Many competitors came from Greek colonies in the Italian peninsula, Asia Minor, and Africa.
3.2 Did athletes receive prizes for winning?
Although the only prize at Olympia was a wreath or garland, Olympic champions received widespread adulation and lavish benefits from their home cities. They also earned substantial prizes for winning at other preliminary festivals.
3.3 What was the significance of nudity in the ancient Olympic Games?
Athletes typically participated in the nude, a practice scholars have attributed to various reasons, including religious rites, social customs, and the demonstration of self-control. While modern Judeo-Christian societies might find public nudity scandalous, ancient Greeks saw nothing shameful about it, especially male nudity.
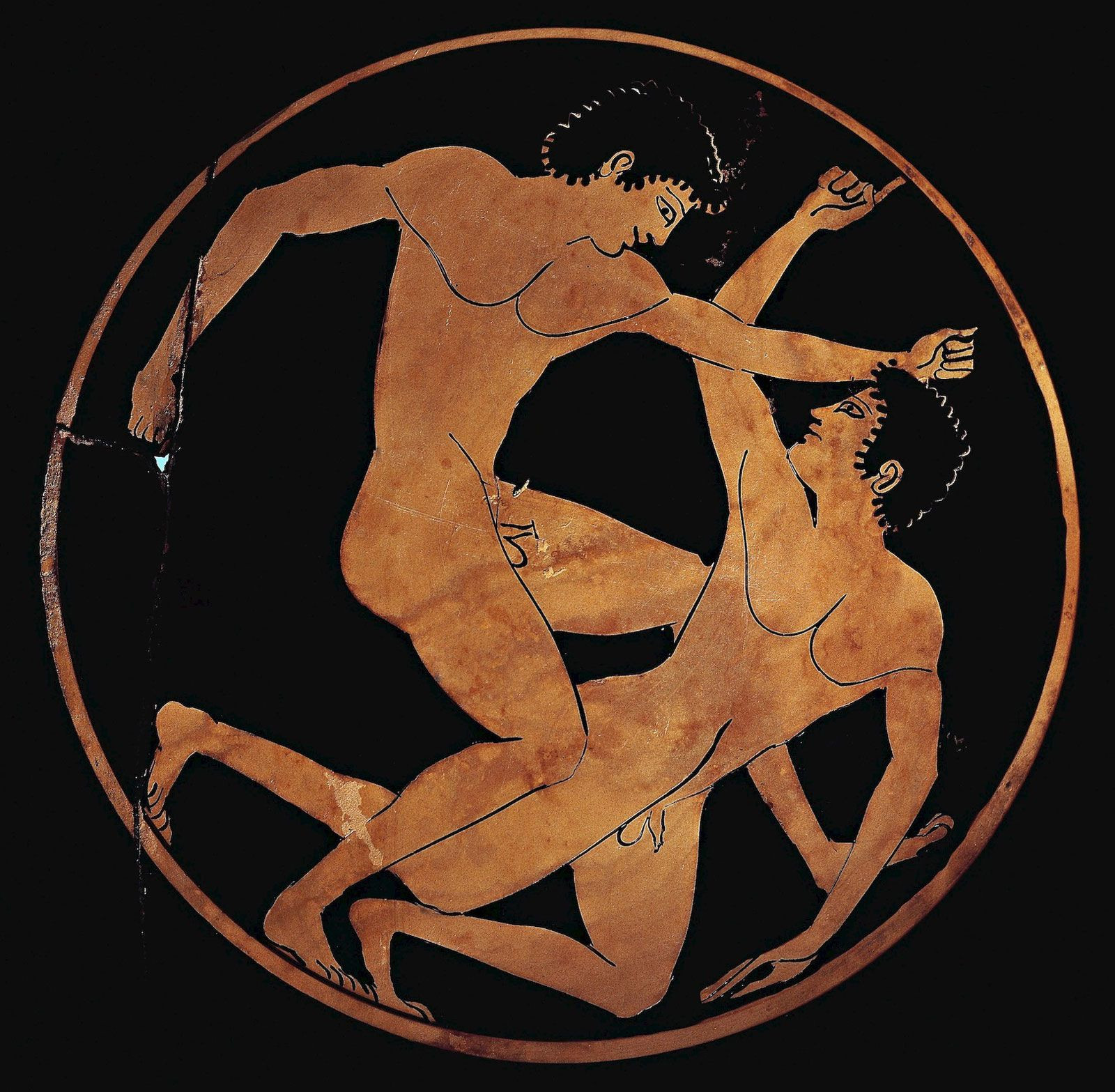 Wrestlers depicted on an ancient Greek cup
Wrestlers depicted on an ancient Greek cup
4. When and why did the ancient Olympic Games decline?
The decline of the ancient Olympic Games began in the Roman era due to political instability, corruption, and a loss of focus on the Games’ original values. The Games were officially banned in 393 AD by Emperor Theodosius I, who sought to suppress pagan festivals. The site of Olympia was further damaged by natural disasters.
4.1 What factors contributed to the decline of the ancient Olympic Games?
Several factors led to the decline:
- Political instability: The Roman era brought political instability and conflicts.
- Corruption: Increased corruption and professionalism undermined the Games’ integrity.
- Loss of values: The Games lost focus on their original religious and ethical values.
4.2 Why were the ancient Olympic Games banned?
In 393 AD, Emperor Theodosius I banned the Olympic Games as part of his efforts to suppress pagan festivals and promote Christianity as the state religion.
4.3 What happened to the site of Olympia after the Games were banned?
After the ban, the site of Olympia suffered damage from earthquakes and floods, leading to its eventual abandonment.
5. How were the modern Olympic Games revived?
The modern Olympic Games were revived in the late 19th century by Baron Pierre de Coubertin, who sought to promote international understanding and peace through athletic competition. The first modern Olympics were held in Athens, Greece, in 1896.
5.1 Who was Baron Pierre de Coubertin, and what was his vision for the Olympic Games?
Baron Pierre de Coubertin was a French educator and historian who believed that the Olympic Games could promote international understanding, peace, and physical fitness. He envisioned a modern revival of the ancient Games that would bring together athletes from all nations.
5.2 When and where were the first modern Olympic Games held?
The first modern Olympic Games were held in Athens, Greece, in April 1896. The Games were a great success, attracting athletes from 14 nations.
5.3 What were some of the challenges faced during the revival of the Olympic Games?
Coubertin faced numerous challenges, including:
- Lack of interest: Initially, many Europeans were uninterested in reviving the Games.
- Funding: Securing financial support for the Games was difficult.
- Logistics: Organizing and coordinating an international sporting event required significant effort.
6. How did the Olympic Games evolve in the 20th and 21st centuries?
The Olympic Games evolved significantly throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. New sports and events were added, the Winter Olympics were established, and the Games became a global media spectacle.
6.1 What were some of the major milestones in the history of the modern Olympic Games?
Key milestones include:
- 1924: The first Winter Olympics were held in Chamonix, France.
- 1960: The Paralympic Games were officially recognized.
- 1984: Los Angeles Olympics marked the beginning of commercial success and financial viability.
- 2000: Sydney Olympics showcased advancements in technology and global participation.
6.2 How did the Winter Olympics come to be?
The concept of Winter Olympics emerged to showcase sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympics were held in Chamonix, France, in 1924, featuring events like skiing, ice hockey, and figure skating.
6.3 How have the Olympic Games become a global media event?
The Olympic Games have transformed into a global media event through television broadcasting, digital media, and social media. The Games attract billions of viewers worldwide, generating significant revenue through advertising and sponsorships.
7. What are some of the controversies and challenges in the modern Olympic Games?
The modern Olympic Games have faced numerous controversies and challenges, including political boycotts, doping scandals, financial issues, and concerns about environmental impact.
7.1 What are some of the political boycotts that have affected the Olympic Games?
Several political boycotts have impacted the Olympic Games:
- 1980 Moscow Olympics: Led by the United States, protesting the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan.
- 1984 Los Angeles Olympics: The Soviet Union and its allies boycotted in retaliation.
7.2 How has doping affected the Olympic Games, and what measures have been taken to combat it?
Doping has been a persistent issue. Organizations like the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) have been established to implement testing and sanctions. High-profile scandals have led to stricter regulations and advanced detection methods.
7.3 What are some of the financial and environmental challenges facing the Olympic Games?
Financial challenges include:
- High costs: Hosting the Olympics can be extremely expensive, leading to debt for host cities.
- Infrastructure: Building new venues and infrastructure is a significant financial burden.
Environmental challenges include:
- Sustainability: Concerns about the environmental impact of constructing venues and hosting large-scale events.
- Carbon footprint: Reducing the carbon footprint of the Games is a growing priority.
8. What is the legacy and impact of the Olympic Games?
The Olympic Games have a lasting legacy and impact on sports, culture, and international relations. They promote athletic excellence, cultural exchange, and global cooperation.
8.1 How do the Olympic Games promote athletic excellence and sportsmanship?
The Olympic Games inspire athletes to achieve their best, fostering a culture of excellence and sportsmanship. The Games provide a platform for athletes to showcase their skills and compete at the highest level.
8.2 What role do the Olympic Games play in cultural exchange and international relations?
The Olympic Games bring together people from different countries, promoting cultural exchange and understanding. The Games can foster goodwill and cooperation between nations, contributing to international peace and diplomacy.
8.3 How do the Olympic Games impact the host cities and countries?
The Olympic Games can have both positive and negative impacts on host cities and countries. Positive impacts include:
- Economic benefits: Tourism, job creation, and infrastructure development.
- Urban renewal: Investment in new facilities and infrastructure can revitalize host cities.
- National pride: Hosting the Games can boost national pride and morale.
Negative impacts include:
- Financial burdens: High costs can lead to debt.
- Displacement: Construction can displace local communities.
- Environmental damage: Infrastructure projects can harm the environment.
9. What are some of the most memorable moments in Olympic Games history?
Olympic Games History is filled with many memorable moments, showcasing human achievement, drama, and inspiration.
9.1 What are some examples of exceptional athletic performances in the Olympic Games?
Exceptional athletic performances include:
- Jesse Owens (1936 Berlin): Won four gold medals in track and field, defying Nazi propaganda.
- Bob Beamon (1968 Mexico City): Set a long jump world record that stood for nearly 23 years.
- Nadia Comăneci (1976 Montreal): Achieved the first perfect 10 in gymnastics.
- Michael Phelps (Multiple Olympics): Won 28 medals in swimming, the most of any Olympian.
- Usain Bolt (2008 Beijing, 2012 London, 2016 Rio): Dominating sprints with world record-breaking performances.
9.2 What are some of the dramatic and emotional moments in Olympic Games history?
Dramatic and emotional moments include:
- Derek Redmond (1992 Barcelona): The British sprinter tore his hamstring during the 400m semi-final but finished the race with his father’s help.
- Kerri Strug (1996 Atlanta): The American gymnast landed her second vault on an injured ankle, securing the gold medal for the U.S. team.
- Ethiopian Marathon Runner Abebe Bikila (1960 Rome): Won a gold medal running barefoot.
9.3 What are some of the inspiring stories of overcoming adversity in the Olympic Games?
Inspiring stories of overcoming adversity include:
- Wilma Rudolph (1960 Rome): Overcame polio to win three gold medals in track and field.
- Anthony Ervin (2000 Sydney, 2016 Rio): Battled mental health issues and addiction to win gold medals in swimming 16 years apart.
- Tanni Grey-Thompson (Paralympics): One of Britain’s most successful Paralympians who won 16 medals after being born with spina bifida.
10. How can you get involved in the Olympic movement?
There are many ways to get involved in the Olympic movement, from participating in sports to volunteering and supporting Olympic athletes.
10.1 How can you participate in sports and athletic activities related to the Olympics?
Participating in sports and athletic activities includes:
- Joining local sports clubs: Engage in sports and develop your skills.
- Participating in community events: Compete in local races, tournaments, and sports festivals.
- Supporting youth sports programs: Encourage young people to get involved in sports.
10.2 How can you volunteer for the Olympic Games or other sporting events?
Volunteering opportunities include:
- Applying to be a volunteer: Support the Games in various roles, such as event management, hospitality, and transportation.
- Helping at local events: Volunteer at community sports events and competitions.
- Supporting sports organizations: Offer your time and skills to assist sports clubs and organizations.
10.3 How can you support Olympic athletes and the Olympic movement?
Supporting Olympic athletes and the movement includes:
- Attending events: Show your support by attending Olympic Games and other sporting events.
- Donating to sports organizations: Contribute to organizations that support athletes and promote sports.
- Promoting Olympic values: Advocate for sportsmanship, fair play, and international understanding.
FAQ about the History of the Olympic Games
1. What was the original purpose of the ancient Olympic Games?
The ancient Olympic Games were held as part of a religious festival to honor Zeus in Olympia.
2. How often were the ancient Olympic Games held?
The ancient Olympic Games were held every four years.
3. What events were included in the ancient Olympic Games?
Events included footraces, wrestling, pentathlon, boxing, chariot racing, and other athletic competitions.
4. Who was eligible to participate in the ancient Olympic Games?
Only freeborn Greek citizens were eligible to participate.
5. When were the ancient Olympic Games banned, and by whom?
The ancient Olympic Games were banned in 393 AD by Roman Emperor Theodosius I.
6. Who revived the modern Olympic Games?
Baron Pierre de Coubertin revived the modern Olympic Games.
7. When and where were the first modern Olympic Games held?
The first modern Olympic Games were held in Athens, Greece, in 1896.
8. What are some of the controversies that have affected the modern Olympic Games?
Controversies include political boycotts, doping scandals, and financial issues.
9. How have the Olympic Games impacted host cities and countries?
The Olympic Games can bring economic benefits, infrastructure development, and national pride but also pose financial and environmental challenges.
10. What is the legacy of the Olympic Games?
The legacy of the Olympic Games includes promoting athletic excellence, cultural exchange, and international cooperation.
Whether you’re an athlete, a sports enthusiast, or someone seeking to understand the historical context of the Olympic Games, we hope this journey through time has been informative and inspiring.
If you’re a Polar device user in the USA seeking reliable support, remember to visit polarservicecenter.net for comprehensive assistance and guidance. With detailed guides, warranty information, and expert support, polarservicecenter.net is your go-to resource for all things Polar. Address: 2902 Bluff St, Boulder, CO 80301, United States. Phone: +1 (303) 492-7080.
Take action now and ensure your Polar device is always at its best by exploring the resources at polarservicecenter.net today!