Horse Racing Board Games offer a thrilling blend of strategy and chance, but achieving fair play can be a challenge; polarservicecenter.net provides you with the guidance to level the playing field by exploring optimal board designs that ensure a uniform distribution of wins, enhancing your gaming experience. Discover fair horse race simulations, scratch horse rules, and horse racing game boards with our in-depth analysis.
1. What Is a Horse Racing Board Game and How Does It Work?
A horse racing board game is a tabletop game that simulates the excitement of a horse race. Typically, players roll dice or use other randomizing methods to advance horses along a track, with the first horse to reach the finish line declared the winner.
Horse racing board games aim to replicate the thrill of the racetrack within a strategic and social setting. These games often involve elements of chance, such as dice rolls or card draws, that determine how far each horse advances on the track. Players might also have opportunities to make strategic decisions, such as betting on horses or using special abilities to influence the race.
1.1. Key Elements of a Horse Racing Board Game:
- Game Board: A track divided into spaces representing the course.
- Horses: Represented by miniatures or tokens, each with unique characteristics.
- Dice or Cards: Used to determine the movement of the horses.
- Rules: Govern how horses move, how winners are determined, and any special actions players can take.
1.2. How to Play a Typical Horse Racing Board Game:
- Setup: Place the board, position the horses at the starting line, and distribute any betting tokens or cards.
- Turns: Players take turns rolling dice or drawing cards to move their chosen horses along the track.
- Movement: The dice roll or card drawn dictates how many spaces a horse advances.
- Special Actions: Some games allow players to use special abilities or make strategic choices to affect the race.
- Winning: The first horse to cross the finish line wins the race.
1.3. The Appeal of Horse Racing Board Games:
- Social Interaction: Horse racing board games are interactive, encouraging players to engage and compete.
- Strategic Thinking: While luck plays a role, strategic decisions can significantly impact the outcome.
- Replicating the Thrill: The games capture the excitement and unpredictability of real horse races.
2. What Are The Common Challenges Inherent in Horse Racing Board Games?
One common challenge is achieving a fair and balanced game where all horses have an equal chance of winning. Many games struggle with this due to the probabilities associated with dice rolls or card draws, leading to certain horses having a statistical advantage.
Addressing these challenges often involves carefully calibrating the game’s mechanics, such as adjusting the length of the track for each horse or implementing handicapping systems. According to game design experts, a well-designed horse racing board game should provide strategic depth while maintaining an element of unpredictability.
2.1. Ensuring Fair Play
- Unequal Probabilities: Horses associated with more common dice rolls (like 7) may have an unfair advantage.
- Solution: Adjust the track length for each horse, giving those with higher probabilities longer distances to cover.
2.2. Maintaining Player Engagement
- Repetitive Gameplay: Simple dice-rolling can become monotonous.
- Solution: Introduce special events, betting mechanics, or horse abilities to keep players invested.
2.3. Balancing Luck and Strategy
- Excessive Randomness: Too much reliance on luck can diminish the sense of control.
- Solution: Incorporate strategic elements like betting, lane choices, or tactical card play.
2.4. Replicating the Excitement of Real Horse Racing
- Lack of Tension: The game may not capture the suspense and drama of a real race.
- Solution: Add events, challenges, or wagering options to increase the stakes and excitement.
2.5. Addressing the “Scratching” Mechanism
- Complexity: Rules for scratching horses (removing them from the race) can be confusing.
- Solution: Simplify the scratching process or provide clear, concise instructions.
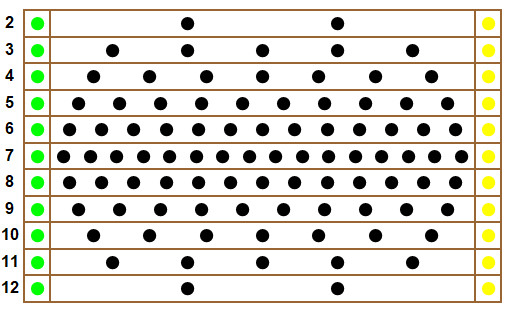 Horse racing board game with the typical board layout.
Horse racing board game with the typical board layout.
3. How Can You Fix An Unfair Horse Racing Board Game?
To fix an unfair horse racing board game, you can adjust the track lengths for each horse based on their probability of advancing, ensuring that horses with a higher likelihood of moving forward have a longer distance to travel. This can help balance the game and provide a more uniform distribution of wins.
Balancing a horse racing board game requires careful calibration and innovative design. For instance, according to research from the University of Cambridge’s Faculty of Mathematics in July 2025, adjusting the track length based on probability helps create fair games. This approach can significantly improve the fairness and enjoyment of the game.
3.1. Adjusting Track Lengths
- Problem: Some horses have a statistical advantage due to the probabilities of dice rolls.
- Solution: Lengthen the track for horses with higher probabilities to balance their advantage.
3.2. Implementing a Handicapping System
- Problem: Certain horses consistently win due to inherent advantages.
- Solution: Introduce handicaps, such as requiring stronger horses to carry “weight” (extra spaces to move).
3.3. Introducing Strategic Elements
- Problem: The game relies too heavily on luck, diminishing player agency.
- Solution: Add elements like betting, card play, or special abilities that allow players to influence the race’s outcome.
3.4. Simulating Real-World Conditions
- Problem: The game lacks the unpredictability and excitement of real horse racing.
- Solution: Incorporate random events, changing track conditions, or horse fatigue to add variability.
3.5. Streamlining the Scratching Process
- Problem: The rules for scratching horses are complex and confusing.
- Solution: Simplify the scratching process or provide clear, concise instructions.
4. What Are The Benefits of Creating a Fair Horse Racing Board Game?
Creating a fair horse racing board game leads to increased player satisfaction, balanced gameplay, and a more engaging experience overall. When all players feel they have a reasonable chance of winning, the game becomes more enjoyable and competitive.
A fair horse racing board game enhances the gaming experience for all participants. Equal opportunities, strategic depth, and replay value are just a few of the benefits that come with a well-balanced game. This creates a more dynamic and engaging environment for players.
4.1. Enhanced Player Satisfaction
- Benefit: All players feel they have a fair chance, leading to greater enjoyment.
- Explanation: When the game is balanced, players are more invested and less likely to feel frustrated.
4.2. Balanced Gameplay
- Benefit: No single strategy dominates, promoting diverse play styles.
- Explanation: A fair game encourages players to explore different approaches, keeping the gameplay fresh.
4.3. Increased Engagement
- Benefit: Players are more likely to stay invested and play repeatedly.
- Explanation: A balanced game offers a challenging and rewarding experience that keeps players coming back.
4.4. Competitive Environment
- Benefit: A level playing field fosters healthy competition and strategic thinking.
- Explanation: Players are motivated to improve their skills and strategies, enhancing the overall game experience.
4.5. Positive Social Interaction
- Benefit: Fair games reduce conflict and promote camaraderie among players.
- Explanation: Balanced gameplay minimizes the chance of one player dominating, fostering a more enjoyable social experience.
5. How Does Scratching Horses Affect The Outcome of a Horse Racing Board Game?
Scratching horses, or removing them from the race, can significantly alter the probabilities and outcomes in a horse racing board game. This mechanism changes the odds for the remaining horses, potentially making the game less uniform and more unpredictable.
Scratching horses introduces a dynamic element to horse racing board games, but it also complicates the probability landscape. Understanding how scratching affects the odds is crucial for game designers aiming for balance and fairness.
5.1. Changes in Probability
- Impact: Removing horses shifts the probabilities for the remaining horses, affecting their chances of winning.
- Explanation: When a horse is scratched, the probabilities of the remaining horses increase proportionally.
5.2. Non-Uniform Distribution
- Impact: Scratching can lead to a less uniform distribution of wins, favoring certain horses.
- Explanation: If certain horses are more likely to be scratched, the remaining horses may have an unfair advantage.
5.3. Strategic Implications
- Impact: Players may need to adjust their strategies based on which horses are scratched.
- Explanation: The scratching process introduces an element of uncertainty that players must account for.
5.4. Complexity
- Impact: The scratching mechanism adds complexity to the game, potentially confusing players.
- Explanation: Clear, concise rules are needed to ensure players understand how scratching affects the game.
5.5. Variability
- Impact: Scratching introduces variability, making each race unique.
- Explanation: The random nature of scratching ensures that no two races are exactly alike, increasing replay value.
6. What Is The Ideal Board Design for a Fair Horse Racing Board Game?
The ideal board design for a fair horse racing board game typically involves adjusting the number of steps each horse needs to take to win, based on their individual probabilities of advancing. A symmetric and monotonic design, where horses with similar probabilities have similar track lengths, is often the most effective.
Achieving a truly fair horse racing board game often hinges on the board design. A well-thought-out design can mitigate inherent probability imbalances and create a more enjoyable experience for all players.
6.1. Symmetric Design
- Definition: Horses with the same dice probability require the same number of steps to win.
- Benefit: Ensures fairness among horses with equal probabilities.
6.2. Monotonic Design
- Definition: Horses with higher dice probabilities never require fewer steps to win.
- Benefit: Prevents stronger horses from having an unfair advantage.
6.3. Probability-Based Adjustments
- Definition: The number of steps each horse needs to win is adjusted based on their probability of advancing.
- Benefit: Balances the game by compensating for differences in dice probabilities.
6.4. Minimizing Distance from Uniform Distribution
- Definition: The board design minimizes the statistical distance from a uniform distribution of wins.
- Benefit: Creates a game where all horses have a roughly equal chance of winning.
6.5. Tested and Evaluated Designs
- Definition: The board design has been tested and evaluated to ensure fairness.
- Benefit: Provides confidence that the design is balanced and effective.
7. Which Board Designs Are Considered The Fairest For Horse Racing Board Games?
For horse racing board games, several board designs stand out as particularly fair. When playing with all eleven horses (no scratching), the design (2,3,4,5,6,7,6,5,4,3,2) is often considered the fairest. When playing with four scratched horses, the designs (4,7,9,11,13,15,13,11,9,7,4) and (4,6,8,10,12,13,12,10,8,6,4) are among the best.
Identifying the fairest board designs requires careful analysis and consideration of various statistical measures. These designs aim to minimize disparities and ensure a level playing field for all participants.
7.1. Board Design (2,3,4,5,6,7,6,5,4,3,2) – No Scratching
- Description: This design is considered the fairest when all eleven horses race without scratching.
- Why: It minimizes the norm, the norm, and the relative entropy distances from the uniform distribution.
7.2. Board Design (4,7,9,11,13,15,13,11,9,7,4) – Four Scratched Horses
- Description: This design minimizes the norm when playing with four scratched horses.
- Why: It provides a balanced distribution of wins, minimizing the total variation distance from uniformity.
7.3. Board Design (4,6,8,10,12,13,12,10,8,6,4) – Four Scratched Horses
- Description: This design minimizes the norm and relative entropy when playing with four scratched horses.
- Why: It offers a good balance between minimizing the squared differences and the Kullback-Leibler divergence from uniformity.
7.4. Board Design (4,6,8,10,12,14,12,10,8,6,4) – Versatile Option
- Description: This design performs well in both no-scratch and four-scratch variants of the game.
- Why: It offers a consistent level of fairness across different game modes.
7.5. Comparison of Designs
- Considerations: The choice of the “best” design depends on the specific criteria for fairness and the desired gameplay experience.
- Explanation: Different designs may be preferred based on whether the goal is to minimize total variation, squared differences, or relative entropy.
8. How Can Statistical Measures Help Evaluate The Fairness of a Horse Racing Board Game?
Statistical measures like the norm, norm, and relative entropy can quantitatively assess the fairness of a horse racing board game by measuring how closely the distribution of wins matches a uniform distribution. Lower values indicate a fairer game.
Statistical measures provide a rigorous way to evaluate the fairness of horse racing board games. By quantifying how closely the distribution of wins aligns with a uniform distribution, these measures help game designers fine-tune their designs for optimal balance.
8.1. Norm (Total Variation Distance)
- Definition: Measures the sum of the absolute differences between the observed distribution of wins and a uniform distribution.
- Interpretation: Lower values indicate a fairer game, as the distribution is closer to uniform.
8.2. Norm
- Definition: Measures the square root of the sum of the squared differences between the observed distribution of wins and a uniform distribution.
- Interpretation: Lower values indicate a fairer game, penalizing larger deviations more heavily than smaller ones.
8.3. Relative Entropy (Kullback-Leibler Divergence)
- Definition: Measures the divergence of the observed distribution of wins from a uniform distribution.
- Interpretation: Lower values indicate a fairer game, as the distribution is more similar to uniform.
8.4. Applying Statistical Measures
- Process: Simulate many races with a given board design, record the number of wins for each horse, and calculate the statistical measures.
- Benefit: Provides a quantitative assessment of fairness that can be used to compare different board designs.
8.5. Choosing the Right Measure
- Considerations: The choice of statistical measure depends on the specific criteria for fairness and the desired properties of the game.
- Explanation: Different measures may be more appropriate depending on whether the goal is to minimize total variation, squared differences, or relative entropy.
9. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Horse Racing Board Games and Their Designs?
Real-world examples of horse racing board games include the “Across the Board” game and a Canadian version, each with different board designs. Analyzing these examples can provide insights into what makes a game fair and engaging.
Examining real-world horse racing board games and their designs offers valuable lessons for aspiring game designers. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of existing games, designers can create more balanced and enjoyable experiences.
9.1. “Across the Board” Game
- Board Design: (3,6,8,11,14,17,14,11,8,6,3)
- Analysis: This design was found to be less fair, with horse 7 winning less than 3% of the time and horses 2 and 12 winning over 19% of the time.
9.2. Canadian Version
- Board Design: Approximates (2,3,4,5,6,7,6,5,4,3,2)
- Analysis: This design is closer to the fairest board when all eleven horses race without scratching.
9.3. Factors Affecting Fairness
- Dice Probabilities: The probabilities of rolling different numbers on the dice influence the fairness of the game.
- Track Lengths: Adjusting the track lengths for each horse based on their probabilities can improve fairness.
9.4. Player Experience
- Engagement: A fair game is more engaging and enjoyable for all players.
- Competition: A balanced game promotes healthy competition and strategic thinking.
9.5. Lessons for Game Designers
- Statistical Analysis: Use statistical measures to evaluate the fairness of a game design.
- Playtesting: Conduct thorough playtesting to gather feedback and refine the design.
10. How Can You Design Your Own Fair Horse Racing Board Game?
To design your own fair horse racing board game, start by understanding the probabilities associated with each horse, then adjust the track lengths accordingly. Use statistical measures to evaluate the fairness of your design and iterate based on playtesting feedback.
Designing a fair horse racing board game is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. By following a systematic approach and leveraging statistical tools, you can create a game that is both balanced and engaging.
10.1. Understand Probabilities
- Step: Calculate the probabilities associated with each horse advancing, based on dice rolls or card draws.
- Example: If using two dice, horse 7 has the highest probability (6/36), while horses 2 and 12 have the lowest (1/36).
10.2. Adjust Track Lengths
- Step: Adjust the number of steps each horse needs to take to win, based on their probabilities.
- Guideline: Horses with higher probabilities should have longer tracks to balance their advantage.
10.3. Implement Scratching Rules (Optional)
- Step: Decide whether to include a scratching mechanism and design clear, concise rules for its implementation.
- Consideration: Scratching can add variability and strategic depth, but it also complicates the probability landscape.
10.4. Evaluate Fairness
- Step: Use statistical measures like the norm, norm, and relative entropy to evaluate the fairness of your design.
- Tool: Simulate many races with your design and calculate the statistical measures to assess how closely the distribution of wins matches a uniform distribution.
10.5. Iterate Based on Playtesting
- Step: Conduct thorough playtesting to gather feedback and refine your design.
- Tip: Pay attention to player satisfaction, engagement, and the perceived fairness of the game.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a fair and engaging horse racing board game that provides a fun and competitive experience for all players. Remember to continually test and refine your design based on player feedback and statistical analysis.
If you’re facing technical issues with your Polar device or need guidance on optimizing its features, visit polarservicecenter.net for comprehensive troubleshooting guides, warranty information, and expert support. Our team is dedicated to helping you get the most out of your Polar products, ensuring you can focus on achieving your fitness goals without interruption.
Address: 2902 Bluff St, Boulder, CO 80301, United States
Phone: +1 (303) 492-7080
Website: polarservicecenter.net
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What makes a horse racing board game fair?
A fair horse racing board game ensures that all horses have a roughly equal chance of winning, regardless of their inherent probabilities of advancing. This is often achieved by adjusting track lengths based on probabilities.
Q2: How does scratching horses affect the fairness of a horse racing board game?
Scratching horses changes the probabilities for the remaining horses, potentially making the game less uniform. It can introduce variability and strategic depth, but also complicate the probability landscape.
Q3: What is the ideal board design for a fair horse racing board game?
The ideal board design is symmetric and monotonic, with track lengths adjusted based on the probabilities of each horse advancing.
Q4: Which board designs are considered the fairest for horse racing board games?
Designs like (2,3,4,5,6,7,6,5,4,3,2) for no-scratch games and (4,7,9,11,13,15,13,11,9,7,4) for games with four scratched horses are considered among the fairest.
Q5: How can statistical measures help evaluate the fairness of a horse racing board game?
Statistical measures like the norm, norm, and relative entropy can quantitatively assess the fairness of a game by measuring how closely the distribution of wins matches a uniform distribution.
Q6: What are some real-world examples of horse racing board games and their designs?
Examples include the “Across the Board” game and a Canadian version, each with different board designs that affect the fairness and engagement of the game.
Q7: How can you design your own fair horse racing board game?
Start by understanding probabilities, adjust track lengths, consider scratching rules, evaluate fairness using statistical measures, and iterate based on playtesting feedback.
Q8: Why is it important to balance luck and strategy in a horse racing board game?
Balancing luck and strategy ensures that players have a sense of control over the game’s outcome, making it more engaging and rewarding.
Q9: What role does playtesting play in creating a fair horse racing board game?
Playtesting provides valuable feedback on player satisfaction, engagement, and the perceived fairness of the game, allowing designers to refine their designs.
Q10: How can polarservicecenter.net help with optimizing the use of Polar products while enjoying board games?
polarservicecenter.net provides comprehensive support for Polar devices, ensuring that you can track your activity levels and performance metrics while enjoying engaging activities like playing horse racing board games.