Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) is a crucial component of Windows Server, designed to broaden single sign-on (SSO) capabilities for end-users, allowing them to securely access applications and resources located outside of the traditional corporate network perimeter. In essence, AD FS extends the reach of your organization’s identity management infrastructure to the cloud and partner networks.
Understanding the Functionality of Active Directory Federation Services
Traditional Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) securely manages user identities (usernames and passwords) and controls access to resources within a Windows domain, providing SSO for applications within that environment. AD FS builds upon this foundation by enabling authentication and authorization for users accessing resources and applications hosted by external entities. This includes scenarios such as accessing a partner organization’s extranet or utilizing services offered by cloud service providers.
AD FS leverages the concept of identity federation to achieve seamless SSO across different security domains. During a single online session, AD FS can authenticate a user to multiple related web applications. It achieves this by securely sharing user identity and access rights, known as “claims,” across organizational boundaries. When a user attempts to access a web application belonging to a trusted business partner (a federation partner), their organization’s AD FS instance authenticates the user’s identity and issues security tokens containing claims. These claims are then presented to the partner’s web application, allowing it to make informed authorization decisions without requiring the user to re-authenticate or manage separate credentials.
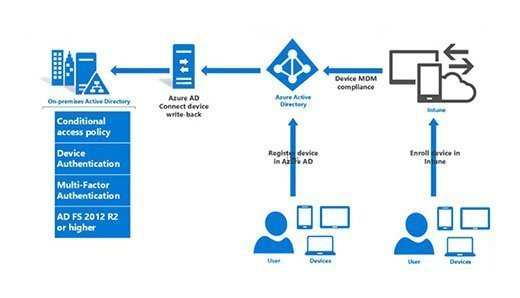 AD FS process
AD FS process
Diagram illustrating the Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) process, showing how user authentication and authorization are handled across different security domains within an enterprise environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing AD FS
Active Directory Federation Services offers compelling benefits, especially in today’s landscape where organizations heavily rely on SaaS applications and web-based services. It significantly simplifies password management, reduces the overhead of managing guest accounts, and enhances security by centralizing authentication processes. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud services and web applications, AD FS becomes even more critical for maintaining a secure and user-friendly access experience. Instead of users managing numerous separate accounts for various SaaS and web apps, AD FS seamlessly links these to their existing organizational credentials. Once a user authenticates with their Windows domain credentials, AD FS automatically handles authentication for all authorized third-party systems.
Benefits of AD FS:
- Simplified User Experience: Users enjoy a seamless SSO experience, eliminating the need to remember multiple usernames and passwords for different applications.
- Centralized Identity Management: IT administrators gain centralized control over user access, simplifying management and enhancing security. Access control policies can be consistently applied across both on-premises and cloud applications.
- Enhanced Security: By federating identity, organizations can reduce the risk associated with managing multiple sets of credentials and improve security posture.
- Streamlined Guest Account Management: AD FS simplifies the process of granting and revoking access for guest users and partners, improving efficiency and security.
- Developer Productivity: Developers can offload authentication complexities to AD FS, allowing them to concentrate on core application development rather than identity management.
- Support for Modern and Legacy Applications: AD FS provides a unified authentication mechanism for both modern web applications and legacy applications, bridging the gap between different technology stacks.
Drawbacks of AD FS:
- Infrastructure Overhead: Implementing AD FS necessitates additional infrastructure components, including federation servers and web application proxies, which can incur setup and maintenance costs.
- Potential Points of Failure: As with any added infrastructure component, AD FS introduces potential points of failure. Careful planning and redundancy are essential to ensure high availability.
- Complexity of Initial Setup: While offering long-term simplification, the initial setup and configuration of AD FS can be complex and require specialized expertise.
Key Features of AD FS
AD FS is equipped with several important features that empower IT teams to implement robust and flexible federated identity solutions.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Federation
The core strength of AD FS lies in its SSO federation capabilities. It allows federation partners to provide a streamlined user experience when accessing an organization’s web applications. Furthermore, organizations can deploy federation servers across multiple partner organizations, facilitating secure transactions and collaborations between them. This cross-organizational SSO is crucial for B2B collaborations and accessing cloud-based services.
Interoperability through Industry Standards
AD FS adheres to the WS-Federation specification, a widely adopted standard for federated identity management. This commitment to standards ensures interoperability with a broad range of products and platforms that support web services architecture. This interoperability extends beyond Microsoft-centric environments, enabling integration with systems that do not rely on the Windows identity model, promoting seamless integration in diverse IT landscapes.
Extensibility and Customization
AD FS is designed for extensibility. It natively supports Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 1.1 and 2.0, a standard XML-based data format for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains. It also supports Kerberos authentication for internal resources. Moreover, AD FS provides customizable claims rules, allowing administrators to tailor the claims issued to applications based on specific organizational needs and security policies. This flexible architecture enables organizations to adapt AD FS to their existing security frameworks and business requirements.
Evolution of AD FS Versions
Since its initial release as an add-on for Windows Server 2003 R2, Active Directory Federation Services has undergone significant evolution, with Microsoft releasing several improved versions.
-
AD FS 2.0: Compatible with Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2, AD FS 2.0, offered as a separate download, brought enhancements like improved installation processes with server validation checks, tighter integration with Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007 and Active Directory Rights Management Services, and a more user-friendly experience for establishing federated trusts.
-
AD FS 3.0 (Windows Server 2012 R2): This version introduced key features such as secure registration and device joining for mobile devices, support for group Managed Service Accounts for simplified service account management, and enhanced customization options for the login experience, catering to the growing mobile workforce and the need for tailored user interfaces.
-
AD FS 4.0 (Windows Server 2016): The latest iteration, AD FS 4.0, further expands capabilities by enabling sign-in with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for enhanced security, support for non-AD Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories for greater flexibility in identity sources, and integration with Windows Hello for Business for modern authentication methods. Microsoft also refined the auditing process, improved SAML interoperability, and enhanced password management features to streamline federation with Microsoft and Office 365 users, reflecting the increasing importance of cloud integration and robust security practices.
By understanding the features and benefits of Active Directory Federation Services, organizations can leverage its power to create a more secure, user-friendly, and efficient access management infrastructure that extends beyond the traditional boundaries of the corporate network.