The Ultimatum Game is an experimental economics tool used to study people’s perceptions of fairness and their willingness to reject unequal offers, and at polarservicecenter.net, we understand the importance of fair play, whether it’s in a game or in getting the most out of your Polar device with our troubleshooting guides, warranty information, and product support. We are here to help you navigate the complexities of your Polar products and ensure you receive fair and reliable service. This principle reflects real-world scenarios, blending behavioral science, decision-making, and fairness perception.
1. What Is the Ultimatum Game?
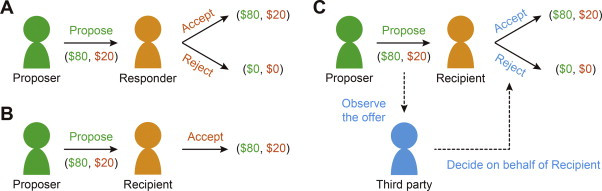
The ultimatum game is a behavioral economics experiment designed to test how people react to fairness and the division of resources. In this game, one player, known as the proposer, is given a sum of money and tasked with dividing it between themselves and another player, the responder. The proposer makes an offer, and the responder then has a choice: accept the offer, in which case the money is divided as proposed, or reject the offer, in which case both players receive nothing.
1.1 How Does the Ultimatum Game Work?
The game’s rules are simple. The proposer decides how to split the money, for example, offering the responder $2 out of a $10 pie. The responder, knowing the total amount and the proposed split, can either accept or reject the offer. A rational, self-interested responder should accept any offer greater than zero, as receiving something is better than nothing. However, numerous studies have shown that people often reject offers they perceive as unfair, even if it means they get nothing.
1.2 What Does the Ultimatum Game Reveal About Human Behavior?
The ultimatum game reveals that people are not always driven by pure self-interest. Instead, concepts like fairness, equity, and a sense of justice play significant roles in decision-making. Many responders reject low offers because they perceive them as unfair, choosing to punish the proposer for an unequal split, even at a cost to themselves.
1.3 How Is the Ultimatum Game Used in Research?
Researchers use the ultimatum game to explore a variety of topics, including:
- Fairness Perceptions: How individuals define and react to fairness.
- Decision-Making Processes: The cognitive and emotional factors influencing choices.
- Cultural Differences: Variations in fairness perceptions across different cultures.
- Social Norms: How societal expectations shape behavior.
- Altruistic Punishment: The willingness to punish unfair behavior, even at personal cost.
1.4 Where Can I Find More Information About Behavioral Economics?
To deepen your understanding, explore resources like “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman, and websites such as the Behavioral Economics Guide. These resources offer comprehensive insights into behavioral economics.
2. What Are the Key Elements of the Ultimatum Game?
Understanding the key elements of the ultimatum game can help you better grasp its implications and how it reflects real-world scenarios.
2.1 The Proposer
The proposer is the player who decides how to split the sum of money. Their offer reflects their perception of fairness, their strategic thinking, and their expectations about what the responder will accept.
2.2 The Responder
The responder is the player who decides whether to accept or reject the proposer’s offer. Their decision reflects their sense of fairness, their willingness to accept unequal outcomes, and their desire to punish unfair behavior.
2.3 The Offer
The offer is the proposed division of the money. It can range from a perfectly equal split (e.g., 50/50) to a highly unequal split (e.g., 90/10). The fairness of the offer is subjective and can be influenced by cultural norms, personal experiences, and individual preferences.
2.4 The Decision
The responder’s decision is the crux of the ultimatum game. Accepting the offer results in both players receiving the proposed amounts. Rejecting the offer results in both players receiving nothing, demonstrating the responder’s willingness to prioritize fairness over personal gain.
2.5 The Stakes
The amount of money being divided can influence the outcome of the game. Higher stakes can lead to more rational behavior, as both proposers and responders may be more motivated to maximize their financial gain.
2.6 What Happens When the Stakes Are Higher?
Research suggests that as the stakes increase, responders are less likely to reject unfair offers. This is because the potential loss of a larger sum of money outweighs the desire to punish the proposer for an unequal split.
3. What Happens in the Brain During the Ultimatum Game?
Neuroscientific studies have shed light on the brain regions involved in decision-making during the ultimatum game, providing insights into the neural basis of fairness and rejection behavior.
3.1 Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (vmPFC)
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is associated with value computation and social emotions. Studies have shown that the vmPFC is more active when responders evaluate fair offers compared to unfair offers. This suggests that the vmPFC plays a role in processing equality and positive emotions associated with fairness.
3.2 Anterior Insula
The anterior insula is linked to negative emotions such as disgust and pain. Research has found that the anterior insula is more active when responders receive unfair offers. This activation is thought to reflect the anticipation of negative emotions and the motivation to avoid unequal social outcomes.
3.3 Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (dlPFC)
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) is involved in cognitive control and decision-making. Studies using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) have shown that disrupting the right dlPFC leads to more frequent acceptance of unfair offers. This suggests that the dlPFC plays a role in enforcing fairness norms and rejecting unequal offers.
3.4 Striatum
The striatum, part of the brain’s reward system, also plays a role. The ventral striatum tracks the equality of offers, while the dorsal striatum may reflect the motivation to punish norm violators.
3.5 How Do Neurotransmitters Affect Decision-Making in the Ultimatum Game?
Pharmacological studies have shown that neurotransmitters like serotonin play a role in processing social equality. Lowering brain serotonin levels increases the rejection rate of unfair offers, suggesting that serotonin modulates retaliatory motivation.
3.6 Where Can I Find More Studies on Brain Activity During the Ultimatum Game?
Explore publications in journals like “Science,” “Nature,” and “Neuron” for detailed neuroscientific studies on the ultimatum game.
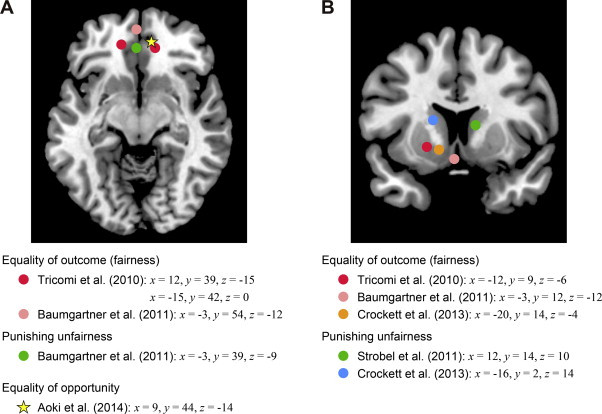 Illustration of a brain showcasing the areas activated during the Ultimatum Game
Illustration of a brain showcasing the areas activated during the Ultimatum Game
4. How Does Culture Influence the Ultimatum Game?
Cultural norms and values significantly influence perceptions of fairness and behavior in the ultimatum game. Research has shown that rejection rates of unfair offers vary widely across different cultures.
4.1 Variations in Fairness Perceptions
In some cultures, fairness may be defined as strict equality, while in others, it may be more flexible, taking into account factors like social status, need, or merit. These differing perceptions can lead to different behaviors in the ultimatum game.
4.2 Impact of Social Norms
Social norms dictate what is considered acceptable behavior in a given society. Cultures with strong norms of cooperation and reciprocity may exhibit higher rejection rates of unfair offers, as individuals are more likely to punish behavior that violates these norms.
4.3 Studies Across Different Cultures
Studies comparing behavior in the ultimatum game across different cultures have revealed significant variations. For example, some studies have found that individuals in Western cultures are more likely to reject unfair offers than those in Eastern cultures.
4.4 How Do Cultural Values Shape Economic Behavior?
Cultural values shape economic behavior by influencing individuals’ preferences, beliefs, and expectations. For example, cultures that emphasize individualism may be more tolerant of inequality, while cultures that emphasize collectivism may be more sensitive to unfairness.
4.5 Where Can I Find Cross-Cultural Studies on the Ultimatum Game?
Search for articles in journals like “American Economic Review” and “Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization” for cross-cultural studies on the ultimatum game.
5. What Are Some Real-World Applications of the Ultimatum Game?
The principles and insights gained from the ultimatum game have numerous real-world applications in fields such as economics, politics, and business.
5.1 Negotiation
The ultimatum game provides valuable insights into negotiation strategies and the importance of fairness in reaching mutually beneficial agreements. Understanding how people react to unequal offers can help negotiators craft proposals that are more likely to be accepted.
5.2 Economics
In economics, the ultimatum game challenges traditional assumptions about rational self-interest and highlights the role of fairness in economic decision-making. It has implications for understanding market behavior, wage negotiations, and resource allocation.
5.3 Politics
The ultimatum game can inform our understanding of political behavior, such as voting patterns, policy preferences, and attitudes toward social inequality. It can help explain why people support policies that promote fairness and equality, even if they do not directly benefit them.
5.4 Business
In business, the ultimatum game can be applied to areas such as pricing strategies, employee compensation, and customer relations. Companies that are perceived as unfair may face negative consequences, such as boycotts or damage to their reputation.
5.5 How Can Businesses Use the Ultimatum Game to Improve Customer Relations?
Businesses can use the ultimatum game’s insights to ensure fair pricing, transparent policies, and equitable treatment of customers, fostering trust and loyalty.
5.6 Where Can I Find Case Studies on the Ultimatum Game in Business?
Explore publications in journals like “Harvard Business Review” and “MIT Sloan Management Review” for case studies on applying the ultimatum game in business contexts.
6. How Does the Ultimatum Game Relate to the Polar Products and Services at polarservicecenter.net?
At polarservicecenter.net, we recognize the significance of equitable and reliable service, similar to the fairness tested in the ultimatum game. We provide clear troubleshooting assistance, warranty details, and dependable product support.
6.1 Providing Fair and Transparent Service
Just as a proposer in the ultimatum game must offer a fair split to avoid rejection, we aim to offer fair and transparent service to our customers. This includes clear communication about repair costs, warranty coverage, and service timelines.
6.2 Ensuring Customer Satisfaction
We understand that customers who feel they have been treated unfairly are likely to reject our services, just as a responder rejects an unfair offer. Therefore, we prioritize customer satisfaction by providing high-quality repairs, responsive support, and a commitment to resolving issues fairly.
6.3 Building Trust and Loyalty
By consistently providing fair and reliable service, we aim to build trust and loyalty with our customers. This is similar to how a proposer who offers a fair split in the ultimatum game is more likely to be accepted and build a positive relationship with the responder.
6.4 What Kind of Support Can I Expect From polarservicecenter.net?
You can expect detailed troubleshooting guides, warranty information, and responsive customer support to ensure your Polar devices are always at their best.
6.5 Where Can I Find More Information About Polar’s Warranty Policies?
Visit the warranty section on polarservicecenter.net to learn more about Polar’s warranty policies and coverage.
 A Polar watch being examined for repair
A Polar watch being examined for repair
7. What Are Some Common Criticisms of the Ultimatum Game?
While the ultimatum game provides valuable insights into fairness and decision-making, it is not without its critics. Some argue that the game’s artificial setting and limited stakes may not accurately reflect real-world behavior.
7.1 Artificial Setting
The ultimatum game is a highly controlled experiment that may not capture the complexity of real-world situations. In real life, decisions are often influenced by a variety of factors, such as social relationships, reputation concerns, and long-term consequences.
7.2 Limited Stakes
The stakes in the ultimatum game are often relatively small, which may not be enough to motivate participants to behave rationally. In real-world situations where large sums of money are involved, people may be more likely to prioritize self-interest over fairness.
7.3 Simplistic Model
The ultimatum game is a simplistic model of human behavior that does not account for individual differences, cultural variations, or contextual factors. Critics argue that the game oversimplifies the decision-making process and ignores important nuances.
7.4 How Do Researchers Address These Criticisms?
Researchers address these criticisms by conducting studies with larger stakes, more realistic settings, and diverse populations, as well as by developing more complex models that account for individual and cultural differences.
7.5 Where Can I Find Discussions on the Limitations of the Ultimatum Game?
Explore academic journals like “Games and Economic Behavior” for discussions on the limitations and potential biases in the ultimatum game.
8. How Can I Use the Principles of the Ultimatum Game in My Daily Life?
Understanding the principles of the ultimatum game can help you make better decisions in your personal and professional life, particularly in situations involving negotiation, conflict resolution, and resource allocation.
8.1 Negotiation Tactics
When negotiating, consider the other party’s perception of fairness and try to craft proposals that are mutually beneficial. Avoid making offers that are too one-sided, as they may be rejected out of principle.
8.2 Conflict Resolution
In conflict situations, strive to find solutions that are fair and equitable to all parties involved. Even if you have the upper hand, consider the other person’s perspective and try to find a compromise that they can accept.
8.3 Resource Allocation
When allocating resources, be mindful of fairness and equity. Distribute resources in a way that is perceived as just, taking into account factors like need, merit, and contribution.
8.4 How Can I Apply Fairness Principles in My Workplace?
You can apply fairness principles in the workplace by ensuring fair compensation, providing equal opportunities, and treating all employees with respect and dignity.
8.5 Where Can I Learn More About Ethical Decision-Making?
Consult resources like “The Power of Ethical Management” by Kenneth Blanchard and Norman Vincent Peale for insights on ethical decision-making.
9. What Are Some Variations of the Ultimatum Game?
Researchers have developed several variations of the ultimatum game to explore different aspects of fairness and decision-making.
9.1 Dictator Game
In the dictator game, one player (the dictator) decides how to split the money, and the other player (the recipient) has no choice but to accept the offer. This game is used to measure altruism and generosity, as the dictator has no incentive to offer anything to the recipient.
9.2 Third-Party Punishment Game
In the third-party punishment game, a third player observes the proposer’s offer and decides whether to punish the proposer for unfair behavior. This game is used to study altruistic punishment, as the third player incurs a cost to punish the proposer, even though they are not directly affected by the offer.
9.3 Trust Game
The trust game involves two players: an investor and a trustee. The investor is given a sum of money and can choose to invest any portion of it with the trustee. The investment is multiplied, and the trustee then decides how much of the multiplied sum to return to the investor. This game is used to measure trust and reciprocity.
9.4 What Do These Variations Reveal About Human Behavior?
These variations reveal that fairness, altruism, and trust play significant roles in human decision-making, even in situations where there is no direct personal benefit.
9.5 Where Can I Find Research on These Game Variations?
Search for articles in journals like “Games and Economic Behavior” and “Journal of Economic Psychology” for research on variations of the ultimatum game.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the Ultimatum Game
Here are some frequently asked questions about the ultimatum game to help you better understand its concepts and implications.
10.1 What is the main purpose of the ultimatum game?
The main purpose is to study how people perceive fairness and make decisions when dividing resources.
10.2 Why do responders often reject unfair offers?
Responders reject unfair offers because they value fairness and are willing to punish proposers for unequal splits, even at a personal cost.
10.3 How does culture influence behavior in the ultimatum game?
Cultural norms and values shape perceptions of fairness, leading to variations in rejection rates across different cultures.
10.4 What brain regions are involved in decision-making during the ultimatum game?
Key brain regions include the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), anterior insula, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC).
10.5 Can the ultimatum game be applied to real-world situations?
Yes, the principles of the ultimatum game can be applied to negotiation, economics, politics, and business to understand and improve decision-making.
10.6 What is the dictator game, and how does it differ from the ultimatum game?
In the dictator game, the recipient has no choice but to accept the offer, unlike the ultimatum game where the responder can reject the offer.
10.7 How do high stakes affect the outcome of the ultimatum game?
Higher stakes generally lead to more rational behavior, with responders being less likely to reject unfair offers due to the potential loss of a larger sum.
10.8 What are some criticisms of the ultimatum game?
Criticisms include the artificial setting, limited stakes, and simplistic model, which may not fully reflect real-world complexities.
10.9 How can businesses use the ultimatum game to improve customer relations?
Businesses can use the ultimatum game to ensure fair pricing, transparent policies, and equitable treatment of customers, fostering trust and loyalty.
10.10 Where can I find support for my Polar product in the USA?
For reliable and fair support for your Polar products, visit polarservicecenter.net, where you can find detailed troubleshooting guides, warranty information, and contact customer support. You can also visit our location at 2902 Bluff St, Boulder, CO 80301, United States or call us at +1 (303) 492-7080.
By understanding the ultimatum game and its applications, you can gain valuable insights into human behavior and make more informed decisions in your daily life. And remember, for fair and reliable support for your Polar products, visit polarservicecenter.net. We are here to help you get the most out of your devices and ensure you receive the service you deserve.
