Are you looking for a fun way to understand trust, security, and rational choices? The Werewolf Game, a social deduction game, offers valuable lessons on these concepts, and at polarservicecenter.net, we’re committed to providing you with the insights to enhance your understanding. With expert advice and support, discover how to apply these principles to real-world scenarios. Enhance your knowledge and skills with our resources on collaboration and negotiation.
1. Understanding the Werewolf Game
What is the Werewolf game, and why is it relevant to understanding trust systems?
The Werewolf game, also known as Mafia, is a social deduction game where players are secretly assigned roles: werewolves or villagers. The villagers must identify the werewolves, who are hidden among them and eliminate them through debate and voting. The game is about uncovering lies and building trust. This game highlights the challenges of discerning truth and falsehood within a group, making it relevant to real-world trust systems.
The game simulates a community infiltrated by a hidden threat. As Bruce Schneier noted, it prompts players to think critically about trust, security, and rational choices. Players must use strategy, observation, and communication to identify the werewolves while the werewolves try to mislead the villagers. The dynamics of the game can teach valuable lessons about how communities form alliances, make decisions, and protect themselves from deception.
1.1. Game Mechanics
How does the game work?
The game involves two alternating phases: night and day. During the night, werewolves choose a villager to eliminate, and special roles like the seer and healer perform their actions. During the day, players debate and vote to eliminate a suspect. The game continues until either all werewolves are eliminated or they outnumber the villagers.
Here’s a breakdown of the roles and their actions:
- Werewolves: These players secretly choose a villager to “murder” each night.
- Villagers: The majority of the players, they must deduce who the werewolves are through discussion and voting.
- Seer: This special role can identify one player each night as either a werewolf or a villager.
- Healer: This role can protect one player each night from being killed by the werewolves.
- Facilitator: This person manages the game, announces phases, and provides information to the special roles.
1.2. Key Strategies in Werewolf
What are some common strategies used by players in the game?
Players employ various strategies, including deception, persuasion, and observation. Villagers often try to identify patterns in behavior, while werewolves attempt to blend in and mislead the group. Effective communication and the ability to read other players are crucial for success. Common strategies include:
- The Seer Strategy: The seer tries to discreetly share information with trusted villagers to build a coalition against the werewolves.
- The Werewolf Blend: Werewolves attempt to mimic villager behavior and avoid suspicion.
- The Noise Strategy: Villagers create “noise” by engaging in general conversation to mask the seer’s communications.
- The Accusation Game: Players try to identify inconsistencies in others’ stories to reveal werewolves.
1.3. Werewolf as a Teaching Tool
How can Werewolf be used as a teaching tool?
Werewolf offers a fun and engaging way to explore concepts related to trust, security, and decision-making. It can be used in educational settings to teach critical thinking, communication, and teamwork. By playing the game, participants can learn to analyze complex social dynamics, identify patterns of deception, and develop strategies for building trust.
The game also highlights the importance of rational decision-making under conditions of uncertainty. Players must weigh the risks and benefits of their actions, consider the potential consequences, and make choices based on limited information. These are valuable skills that can be applied to a wide range of real-world situations.
2. Lessons From Werewolf
What are the key lessons that can be learned from playing Werewolf?
Werewolf offers several valuable lessons applicable to real-world scenarios, including the importance of trust, the challenges of identifying deception, and the need for rational decision-making. Here are some typical strategies:
2.1. The “Kill the Newbies” Strategy
Why are new players often targeted in Werewolf?
New players are often targeted because they are unfamiliar with the game’s strategies and tactics, making them a liability to the group. Eliminating them is seen as a rational choice to improve the group’s odds of success. This behavior, while seemingly unfair, illustrates how groups may prioritize established members over newcomers in situations where trust is critical.
This strategy highlights the challenges faced by newcomers in any community or network. New members may be viewed with suspicion or excluded from important decision-making processes until they have proven their trustworthiness. Overcoming this barrier requires new members to quickly learn the rules and norms of the group, build relationships with established members, and demonstrate their commitment to the group’s goals.
2.2. The Importance of Noise
How does “noise” help protect the seer in Werewolf?
“Noise,” or unnecessary communication, helps to anonymize the seer’s communications, making it harder for the werewolves to identify and target them. By having everyone engage in conversation, the seer can discreetly share information without drawing attention to themselves. This illustrates how creating a high level of activity can mask important signals and protect sensitive information.
This strategy has implications for cybersecurity and counter-surveillance. For example, organizations may use decoy traffic or encryption to mask sensitive communications and protect them from eavesdropping. Similarly, individuals may use pseudonyms or anonymization tools to protect their privacy online. The key is to create a level of “noise” that makes it difficult for attackers to identify and target specific individuals or data.
2.3. Structured and Random Stress Tests
How can structured and random stress tests reveal werewolves?
Stress tests, such as asking players to introduce themselves and state their role, can reveal inconsistencies in behavior that indicate deception. Werewolves may stumble over their words, omit their role, or display other signs of nervousness. This strategy highlights the importance of consistency and ritual in building trust.
This strategy has applications in various fields, including law enforcement, security, and human resources. For example, police officers may use interrogation techniques to stress suspects and elicit confessions. Similarly, security professionals may conduct penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities in computer systems. In human resources, employers may use background checks and interviews to assess the trustworthiness of potential employees.
3. Applying Werewolf Strategies to Real-World Scenarios
How can the strategies used in Werewolf be applied to real-world situations?
The strategies used in Werewolf can be applied to a variety of real-world situations, including cybersecurity, organizational management, and social interactions.
3.1. Cybersecurity
How can Werewolf strategies enhance cybersecurity practices?
In cybersecurity, the “kill the newbies” strategy can be seen as isolating new or compromised nodes to prevent further damage to the network. The “noise” strategy can be applied by using encryption and decoy traffic to mask sensitive communications. Stress tests can be used to identify vulnerabilities in systems and detect malicious activity.
For example, organizations can implement intrusion detection systems that monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and automatically isolate compromised devices. They can also use encryption to protect sensitive data from being intercepted by attackers. Regular security audits and penetration tests can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that systems are secure.
3.2. Organizational Management
How can Werewolf strategies improve organizational management?
In organizational management, understanding group dynamics and identifying potential threats is crucial. The lessons from Werewolf can help managers build trust within their teams, detect deception, and make informed decisions.
For example, managers can use team-building exercises to foster trust and communication among team members. They can also implement policies and procedures to prevent fraud and misconduct. Regular performance reviews and feedback sessions can help identify potential problems and address them before they escalate.
3.3. Social Interactions
How can Werewolf strategies inform social interactions?
In social interactions, the ability to read people and detect deception is valuable. The strategies used in Werewolf can help individuals navigate complex social situations and build stronger relationships.
For example, paying attention to nonverbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, can help individuals detect when someone is being dishonest. Asking clarifying questions and seeking additional information can help verify the truthfulness of statements. Building a network of trusted friends and advisors can provide support and guidance in difficult situations.
4. The Role of Structure in Building Trust
How does the structure of a community or network affect its ability to build trust?
The physical setup of the game influences the dynamics. In a structured setting, like a table, communication is limited, making it easier for the seer to build a trusted network. In unstructured settings, werewolves have an advantage. Structure can provide a framework for building trust. A well-defined structure can make it easier to build trust within a community or network. Clear roles, responsibilities, and communication channels can help members understand their place within the group and how to interact with others.
When structure is lacking, it can be more difficult to build trust. Unclear roles and responsibilities can lead to confusion and conflict. Lack of communication can create misunderstandings and mistrust. In such situations, it may be necessary to establish a more structured environment to facilitate trust-building.
4.1. Structured vs. Unstructured Groups
How do structured and unstructured groups differ in their ability to build trust?
Structured groups, with clear roles and communication channels, facilitate trust-building. Unstructured groups, where communication is less defined, may favor those who can manipulate the environment, such as werewolves.
For example, a sports team is a structured group with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Each player knows their position and what they are expected to do. Communication is typically direct and focused on achieving the team’s goals. This structure makes it easier for players to trust one another and work together effectively.
In contrast, a social gathering may be an unstructured group with no clear roles or responsibilities. Communication is more informal and spontaneous. While this can be a fun and relaxing environment, it may be more difficult to build trust and achieve specific goals.
4.2. The Importance of Rigidity
How can rigidity in a community’s structure aid in trust-building?
Rigidity, or consistency, in the structure of a community or network can make it easier to build trust. When roles, rules, and procedures are clearly defined and consistently enforced, members are more likely to trust one another. This is because they know what to expect and can rely on the system to be fair and predictable.
For example, a court of law is a rigid system with clearly defined rules and procedures. Judges, lawyers, and juries all have specific roles and responsibilities. Evidence is presented according to strict rules of admissibility. Decisions are based on legal precedent and are subject to appeal. This rigidity helps ensure that justice is served fairly and consistently.
4.3. Adapting to Unstructured Environments
What strategies can be used to build trust in unstructured environments?
In unstructured environments, it is important to establish clear communication channels and build relationships with other members. This may involve taking the initiative to organize activities, facilitate discussions, and promote collaboration. It is also important to be transparent and honest in all interactions.
For example, in a new workplace, it may be helpful to introduce yourself to your colleagues and learn about their roles and responsibilities. You can also volunteer to participate in team projects and social events. By demonstrating your willingness to collaborate and contribute, you can build trust and establish yourself as a valued member of the team.
5. Conclusion
What are the key takeaways from using the Werewolf game as a model for understanding trust and security?
The Werewolf game provides valuable insights into trust, security, and rational decision-making. By understanding the strategies and dynamics of the game, individuals and organizations can improve their ability to build trust, detect deception, and protect themselves from threats. Whether it’s in cybersecurity, organizational management, or social interactions, the lessons from Werewolf can help navigate complex situations and make informed choices.
At polarservicecenter.net, we are dedicated to providing you with the resources and support you need to enhance your knowledge and skills in these areas. Explore our website for more information on trust-building strategies, security best practices, and decision-making techniques. Our goal is to empower you to make informed choices and build stronger, more resilient communities and networks.
Remember, the principles learned from Werewolf can be applied to many aspects of life. By understanding the dynamics of trust and deception, you can better navigate the complexities of the world around you.
Address: 2902 Bluff St, Boulder, CO 80301, United States.
Phone: +1 (303) 492-7080.
Website: polarservicecenter.net.
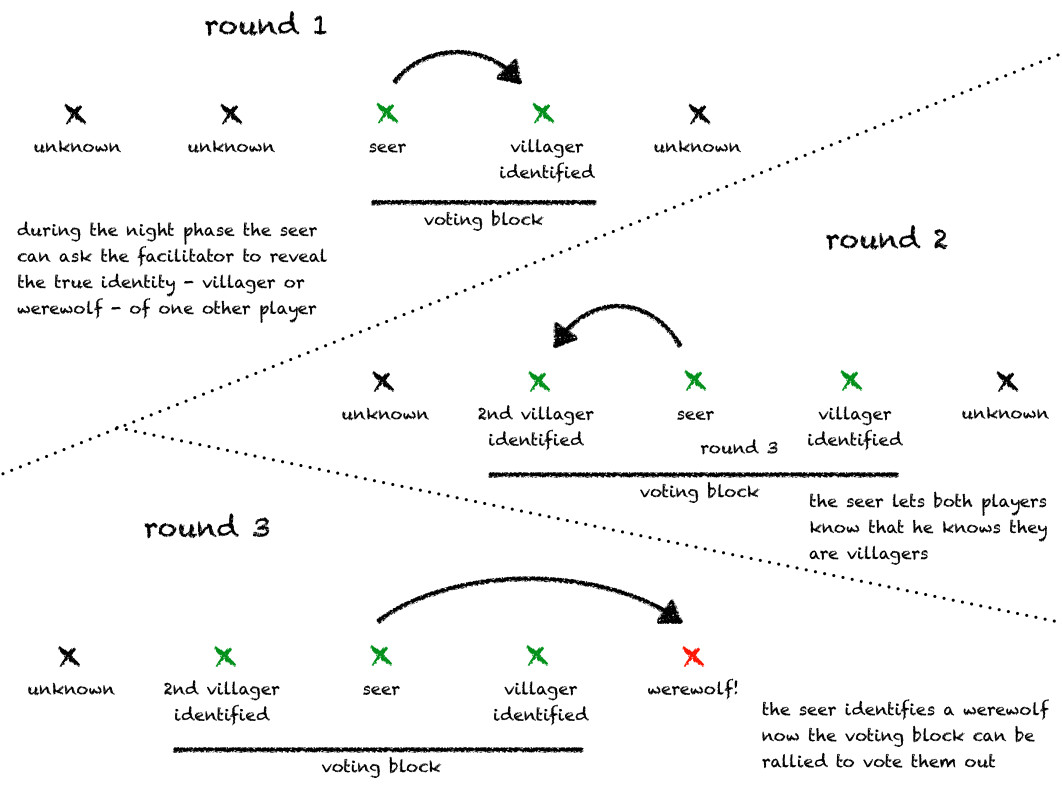 werewolf seer strategy2
werewolf seer strategy2
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Werewolf Game and Trust
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Werewolf game and its implications for understanding trust:
6.1. What is the main objective of the Werewolf game?
The main objective for the villagers is to identify and eliminate all the werewolves, while the werewolves aim to outnumber the villagers.
6.2. How does the seer role help the villagers in the Werewolf game?
The seer can identify one player each night as either a werewolf or a villager, providing crucial information for the villagers to make informed decisions.
6.3. Why is trust so important in the Werewolf game?
Trust is essential because villagers must rely on each other to share information and vote out the werewolves. Without trust, the werewolves can easily manipulate the villagers.
6.4. What are some common tactics used by werewolves to deceive villagers?
Werewolves often try to blend in with the villagers, accuse innocent players, and create confusion to protect their identity.
6.5. How can the “kill the newbies” strategy be justified in the Werewolf game?
New players may be targeted because they are unfamiliar with the game’s strategies, making them a potential liability to the group. Eliminating them is seen as a rational choice to improve the group’s odds of success.
6.6. What does the “noise” strategy achieve in the Werewolf game?
The “noise” strategy helps protect the seer by masking their communications, making it harder for the werewolves to identify and target them.
6.7. How can stress tests help reveal werewolves in the game?
Stress tests, such as asking players to introduce themselves, can reveal inconsistencies in behavior that indicate deception.
6.8. Can the strategies used in Werewolf be applied to real-world situations?
Yes, the strategies used in Werewolf can be applied to various real-world situations, including cybersecurity, organizational management, and social interactions.
6.9. How does structure influence trust-building in the Werewolf game and in real life?
Structure, such as clear roles and communication channels, facilitates trust-building. In unstructured environments, it is more difficult to build trust.
6.10. Where can I find more resources on building trust and detecting deception?
You can find more resources on building trust and detecting deception at polarservicecenter.net, where we offer expert advice and support on these topics.
By exploring these FAQs, you can gain a deeper understanding of the Werewolf game and its implications for understanding trust, security, and decision-making. Remember to visit polarservicecenter.net for more valuable insights and resources.