In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses of all sizes rely heavily on their information technology (IT) infrastructure to operate efficiently and stay competitive. However, managing this complex IT environment can be challenging, resource-intensive, and often distracts from core business objectives. This is where a Managed Service Provider (MSP) steps in as a crucial partner.
An MSP is a third-party company that proactively manages and supports a customer’s IT infrastructure and end-user systems remotely. Think of an MSP as your outsourced IT department, handling everything from network management and cybersecurity to data backup and cloud services. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), non-profit organizations, and even large enterprises are increasingly turning to MSPs to streamline their IT operations, enhance security, and drive business growth. Instead of reacting to IT problems as they arise, MSPs provide proactive and preventative services, ensuring smooth and secure IT operations around the clock.
 Benefits of MSPs in an IT environment
Benefits of MSPs in an IT environment
The Role of a Managed Service Provider: What Do They Do?
Managed service providers offer a wide array of services tailored to meet the diverse IT needs of businesses. These services are designed to offload the burden of day-to-day IT management, allowing organizations to focus on strategic initiatives and core competencies. Here are some key areas where MSPs provide significant value:
-
Network and Infrastructure Management: MSPs take responsibility for the health and performance of your entire IT infrastructure, including networks, servers, and hardware. This involves continuous monitoring, maintenance, and optimization to ensure systems are running smoothly and efficiently. They handle tasks like network configuration, server administration, and performance tuning, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
-
Cybersecurity Services: In an era of escalating cyber threats, security is paramount. MSPs offer comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, including threat detection and prevention, firewall management, intrusion detection systems, vulnerability assessments, and security awareness training for employees. They help businesses establish robust security postures and protect sensitive data from evolving cyber risks.
-
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM): A cornerstone of MSP operations is the use of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools. These platforms allow MSPs to remotely monitor client systems in real-time, identify potential issues before they cause disruptions, and perform proactive maintenance and updates. RMM enables efficient troubleshooting, patch management, and overall system health management from a central location.
-
Cloud Services Management: As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, managing cloud environments becomes crucial. MSPs provide expertise in cloud technologies, assisting with cloud migrations, managing cloud infrastructure, optimizing cloud spending, and ensuring data security and compliance in the cloud. They can manage various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
-
Help Desk and Technical Support: MSPs offer dedicated help desk services to provide end-user support. This includes troubleshooting technical issues, resolving software problems, assisting with hardware malfunctions, and providing general IT guidance to employees. Having a readily available and responsive help desk ensures employees can quickly resolve IT issues and minimize disruptions to their workflow.
-
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Data loss can be catastrophic for any business. MSPs implement robust data backup and disaster recovery solutions to protect critical business information. This includes regular data backups, secure storage, and disaster recovery planning to ensure business continuity in the event of data loss, system failures, or natural disasters.
-
Compliance and Risk Management: Many industries are subject to strict regulatory compliance requirements. MSPs can help businesses navigate these complexities by implementing security controls, policies, and procedures that align with industry regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. They also assist with risk assessments and develop strategies to mitigate IT-related risks.
How Does a Managed Service Provider Work?
The engagement with a managed service provider typically begins with a thorough assessment of the organization’s current IT environment and business objectives. This assessment helps the MSP understand the specific needs and challenges of the client and develop a tailored service plan. The MSP then works in close collaboration with the client, often acting as an extension of their internal team.
Key elements of how MSPs operate include:
-
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): The relationship between an MSP and its client is formalized through a Service Level Agreement (SLA). This contractual document clearly defines the services to be provided, performance metrics, response times, responsibilities of both parties, and pricing terms. SLAs ensure clarity and accountability in the service delivery process.
-
Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance: MSPs utilize RMM tools to proactively monitor client systems 24/7. This allows them to detect potential issues early, often before they impact users. Proactive maintenance, including software updates, patching, and system optimization, is performed regularly to prevent problems and maintain system performance.
-
Remote and On-site Support: MSPs primarily deliver services remotely, leveraging technology to manage and support IT systems efficiently. However, many MSPs also offer on-site support when necessary, particularly for hardware issues or situations requiring physical intervention.
-
Professional Services Automation (PSA) Tools: In addition to RMM, MSPs utilize Professional Services Automation (PSA) tools to streamline their own operations. PSA software assists with project management, ticketing, billing, client communication, and reporting. This enables MSPs to manage their services effectively and provide transparent reporting to clients.
-
Subscription-Based Model: The majority of MSPs operate on a subscription-based pricing model. Clients pay a recurring fee, typically monthly, for a defined set of services. This predictable cost structure allows for better IT budgeting and eliminates the unpredictable expenses associated with break-fix IT models.
 Benefits of MSPs in an IT environment
Benefits of MSPs in an IT environment
Exploring Different Types of Managed Service Providers
The MSP landscape is diverse, with providers specializing in different areas and catering to various client needs. MSPs can be categorized based on the services they offer, the size of clients they serve, or their service delivery model. Here are some common classifications:
Based on Service Focus:
-
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs): MSSPs specialize in cybersecurity services. They offer in-depth security expertise and a wide range of security-focused services like threat intelligence, security monitoring, incident response, and compliance management.
-
Cloud MSPs: These MSPs focus on cloud services, assisting businesses with cloud adoption, migration, management, and optimization. They have expertise in various cloud platforms and help clients leverage the benefits of cloud computing.
-
Communication MSPs: These providers specialize in managing communication systems, such as VoIP, unified communications, and video conferencing solutions. They ensure reliable and efficient communication infrastructure for businesses.
-
Infrastructure MSPs: These MSPs focus on the core IT infrastructure, providing services like server management, network management, data center management, and storage management.
Based on Client Size and Service Scope:
-
Pure-Play MSPs: Often smaller providers, pure-play MSPs typically focus on specific niche services, such as network monitoring or application performance management. They may offer highly specialized expertise in a limited service area.
-
Staffing Legacy MSPs: These MSPs target mid-sized to large enterprises and offer a broader range of services. They can provide comprehensive IT outsourcing, including monitoring, support, software deployment, and project-based services.
-
High-Level MSPs: These MSPs, regardless of size, offer the most comprehensive outsourcing capabilities. They can essentially function as a complete outsourced IT department, managing all aspects of a client’s IT operations.
Key Benefits of Partnering with a Managed Service Provider
Choosing to work with a managed service provider offers numerous advantages for businesses seeking to optimize their IT and achieve strategic goals. The benefits extend beyond just cost savings and encompass improved efficiency, security, and focus.
-
Reduced IT Costs: Outsourcing IT to an MSP can be more cost-effective than maintaining a large in-house IT department. MSPs leverage economies of scale, shared resources, and proactive management to deliver services efficiently and at a predictable cost. Subscription-based pricing helps control IT spending and avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Access to Specialized Expertise: MSPs employ teams of IT professionals with diverse skills and certifications across various technologies. By partnering with an MSP, businesses gain access to a wider pool of expertise than they might be able to afford or attract in-house. This expertise ensures best practices are followed and complex IT challenges are effectively addressed.
-
Enhanced Security Posture: MSPs are at the forefront of cybersecurity best practices and threats. They invest in advanced security tools, stay updated on the latest threats, and implement robust security measures to protect client data and systems. This proactive security approach significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
-
Improved Uptime and Reliability: Proactive monitoring, preventative maintenance, and rapid response to issues ensure higher system uptime and reliability. MSPs minimize downtime, which translates to increased productivity and business continuity.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: MSPs offer scalable IT solutions that can adapt to the changing needs of a business. Whether a company is growing rapidly or experiencing seasonal fluctuations, MSPs can adjust services and resources accordingly, providing the flexibility to scale IT up or down as needed.
-
Focus on Core Business Objectives: By outsourcing IT management to an MSP, businesses free up internal resources and personnel to focus on their core competencies, strategic initiatives, and revenue-generating activities. This allows leadership and employees to concentrate on driving business growth and innovation.
-
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: MSPs provide robust data backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring business continuity in the face of unforeseen events. Having a well-defined disaster recovery plan and reliable backup systems minimizes downtime and data loss, safeguarding the business’s future.
Considerations and Challenges When Choosing an MSP
While the benefits of MSPs are compelling, it’s important to acknowledge potential challenges and considerations when selecting a provider. Careful due diligence and a clear understanding of your needs are crucial for a successful MSP partnership.
-
Security Concerns (If Not Vetted Properly): Entrusting a third party with your IT infrastructure requires careful vetting. Not all MSPs have the same level of security expertise or commitment to security best practices. It’s crucial to choose an MSP with a strong security focus, proven track record, and relevant security certifications.
-
Dependency on a Third-Party: Outsourcing IT naturally creates a dependency on the MSP. If the MSP experiences service disruptions or fails to meet SLA commitments, it can impact the client’s operations. Therefore, selecting a reliable and reputable MSP with robust infrastructure and service delivery processes is essential.
-
Response Time Variability: While SLAs define response times, actual response times can sometimes vary depending on the MSP’s workload and the severity of the issue. Clearly defined escalation procedures and communication protocols in the SLA are important to address this potential challenge.
-
Potential Upselling: Some less scrupulous MSPs may attempt to upsell clients on services or technologies they don’t truly need. A transparent and trustworthy MSP will prioritize the client’s best interests and provide recommendations based on genuine needs, not just sales targets.
-
Data Access and Control: Organizations need to ensure they maintain appropriate access to and control over their data when working with an MSP. Clearly defined data ownership, access policies, and data security measures in the contract are crucial to address concerns about data privacy and control.
Understanding MSP Pricing Models
Managed service providers offer various pricing models to accommodate different client preferences and service requirements. Understanding these models is essential for budgeting and selecting the most suitable option.
-
Per-Device Pricing: This model charges a fixed monthly fee for each device managed, such as computers, servers, or network devices. It’s simple to understand and budget for, particularly for organizations with a relatively stable number of devices.
-
Per-User Pricing: This model charges a flat fee per user per month. It’s well-suited for organizations with users who utilize multiple devices, as it simplifies billing based on the number of users supported, rather than the number of devices.
-
All-Inclusive Pricing (All-You-Can-Eat): This model offers a comprehensive, fixed monthly fee for unlimited IT support and management services, covering the entire IT infrastructure. It provides predictable budgeting and unlimited access to support, but may be more expensive if IT needs are relatively low.
-
Tiered Pricing: This model offers different service packages or tiers at varying price points. Clients can choose the tier that best aligns with their service requirements and budget. Tiers typically differ in terms of service scope, response times, or included features.
-
Monitoring-Only Pricing: This model focuses solely on providing monitoring and alerting services. The MSP monitors the client’s IT infrastructure and alerts them to potential issues, but the client handles the actual remediation and support. It’s a lower-cost option for organizations with some in-house IT capabilities.
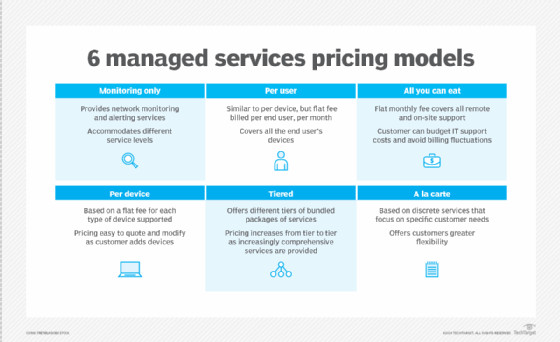 MSP pricing models
MSP pricing models
In conclusion, managed service providers have become indispensable partners for businesses seeking to optimize their IT, enhance security, and focus on strategic growth. By understanding the role of MSPs, their service offerings, benefits, and considerations, organizations can make informed decisions about leveraging managed services to achieve their business objectives in the dynamic digital age. As technology continues to evolve, the strategic importance of MSPs will only continue to grow, making them a vital asset for businesses of all sizes.
